Understanding Type 1 Diabetes-
Understanding Type 1 Diabetes is important to help in prevention of the disease.
Diabetes is defined as an uncontrolled increase in blood glucose levels.
EPIDEMIOLOGY-
Type 1 diabetes is a type of diabetes that is mostly seen in children or the young population but in some cases can occur at any age.
It is more common in the male population in comparison with females.
A family history of diabetes especially a diabetic father is more commonly seen in young diabetic children.
Low birth weight babies are at higher risk for developing Type 1 diabetes.
TYPE 1 DIABETES PATHOLOGY –
The HLA (Human leukocyte antigen) gene located on the short arm of chromosome 6 is most commonly linked to this type of diabetes.
Viral infections like rubella, and mumps can also cause type 1 diabetes.
The beta cells of the pancreas is important because they produce insulin which helps to regulate the blood sugar level of the body.
The combination of viral infections and the genetic factor of the HLA gene leads to the activation of the immune system to act on the beta cells of the pancreas which destroys these cells due to autoimmunity. This causes a decrease in insulin level and the person’s sugar level spikes.
CLINICAL FEATURE-
Mostly the patient remains without any symptoms even after suffering from type 1 diabetes and sudden viral infections can cause the blood glucose levels to increase and the patient can present with a serious complaint like difficulty in breathing, dizziness, or even unconsciousness if blood glucose level is not controlled as the patient develops diabetic ketoacidosis.
In less serious cases the patient can complain of increasing frequency of urination ( polyuria), increased thirst (polydipsia), feeling lethargic, and weight loss.
INVESTIGATION-
Type 1 Diabetes blood investigation-
1) History taking especially family history is very important to diagnose Type 1 diabetes.
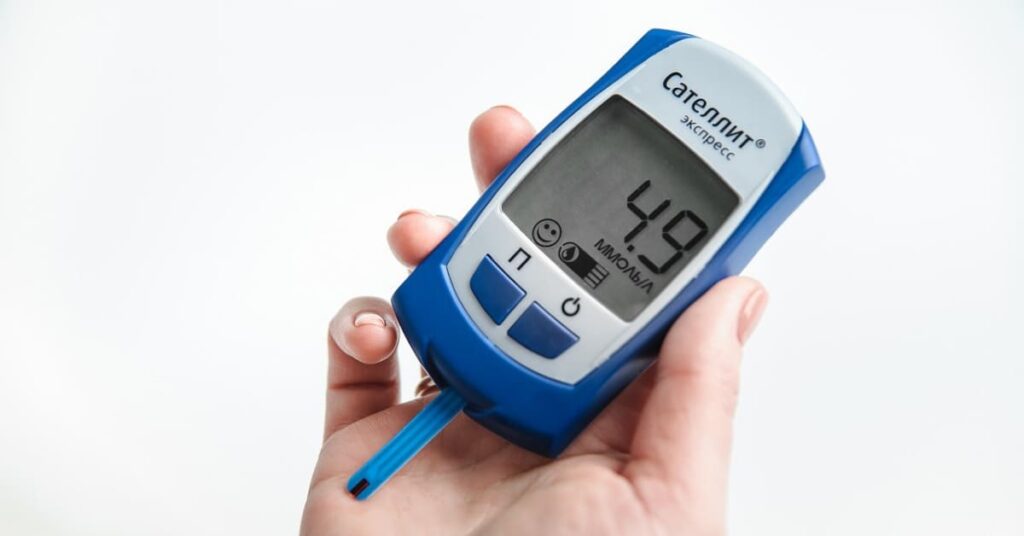
2) Serum blood glucose level which includes both fasting and post-prandial test should be done.
3) HbA1c should be measured too.
4) Urine glucose and ketone should be checked.
5) Sometimes Anti-glutamic acid decarboxylase antibodies should be done.
TREATMENT-
1) Daily glucose monitoring is essential to track disease progression and medication effectiveness.
2) Insulin is the first line of treatment for these patients. Due to the loss of the beta cell of the islet of Langerhans, the insulin-producing capacity of the body is lost and hence insulin replacement is needed.
Insulin is of basal and prandial type.
Basal insulin are glargine, detemir, NPH.
Prandial insulin are lispro, aspart.
Insulin dose is around 0.3 to 1 unit/kg/day but it is calculated on an individual basis keeping in mind their daily activity, diet, any other disease, and many more factors.
3) It is important to eat a healthy diet and cut down on sugar to keep the blood sugar level in control.
4) Exercise is also important as good physical activity helps to keep blood sugar levels at the desired level.
5) Pancreas transplantation is needed in patients whose blood sugar levels don’t come under control after trying all the above-mentioned treatment methods.
TAKE HOME MESSAGE-
1) If you have a family history of diabetes then always get checked by a doctor to prevent any serious consequences.
2) If a person is diabetic or at high risk of diabetes then it is important to consult the doctor if gets any flu-like symptoms such as fever, or cough because these infections act as a trigger factor for type 1 diabetes.
3) Early diagnosis and regular medication as prescribed by the doctor are the mainstay of the treatment for type 1 diabetes.
4) A healthy and active life is possible for type 1 diabetic patients if they include a healthy lifestyle as mode of life.
STAY ACTIVE AND STAY SAFE.






Very informative.keep posting more
You have worked pleasantly with your experiences. Loads of significant information can be taken from your article. Truly it is a huge article for us.How Stem Cells Help Diabetes