RENAL FUNCTION TEST:
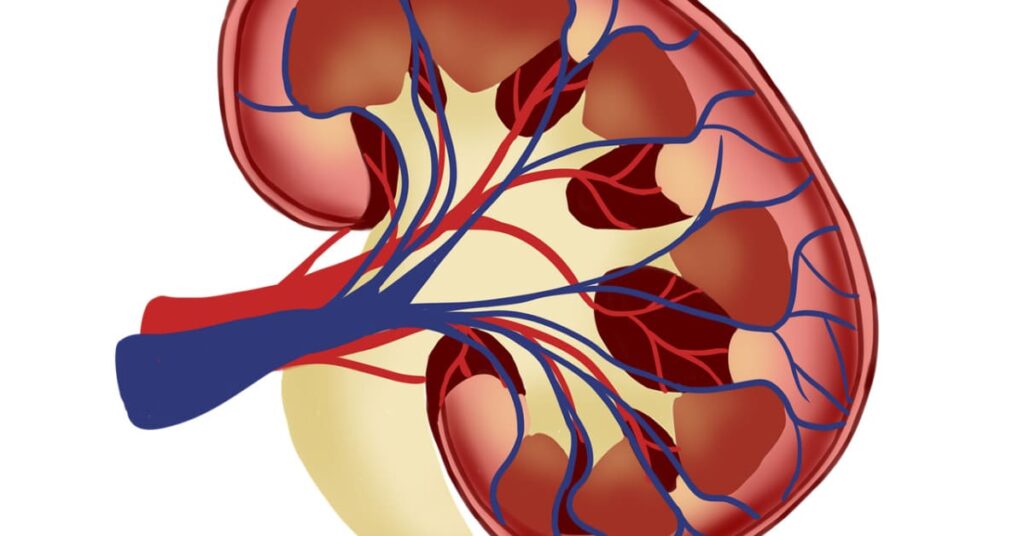
Renal function-
The kidney is an important organ in the body and has many important roles which include:
1) Removal of the waste products produced from the body.
2) Maintaining the level of the electrolyte in the body.
3) Production of renin is an important factor in the maintenance of blood pressure.
4) Production of erythropoietin which has a role in erythropoiesis that is the production of red blood cells.
5) Kidney plays a role in maintaining a balance between acid and base in the body by excretion of hydrogen and bicarbonate ions.
Whenever a person suffers from any renal disease then the kidney is not able to perform these functions and if the disease is not diagnosed early then it can lead to serious kidney problems which include kidney failure.
To check the working status of the kidney various tests can be used and today we will discuss how we can check the kidney function by renal function test.
When a patient visits the doctor, before ordering any test the doctor starts with the proper history taking which includes current symptoms experienced by the patient, duration of the symptoms, past medical history, and family medical history.
After this, the doctor performs various relevant physical examinations, and with the combination of history and physical examination along with the vital parameters, the doctor makes various differential diagnoses.
After this, the doctor orders various types of tests to check the renal function and make a proper diagnosis of the disease so that the proper treatment of the patient can be started.
BLOOD TEST IN RENAL FUNCTION TEST:
1) Haemoglobin level: Anaemia is common in patients suffering from renal problems because of a decrease in the erythropoietic function of the kidney.
2) Erythrocyte sedimentation rate (ESR) – values of ESR are on the higher side which can be due to anemia or inflammatory process.
3) Blood urea: The food that we eat is broken down and one of its products is ammonia which is dangerous to the human body, this ammonia is converted to urea in the liver which is less harmful, and from the liver, it is transported to the kidney which helps in its excretion. In cases of renal disease, blood urea can increase above the normal level.
4) Serum creatinine: creatinine level can increase in blood in case of acute or chronic kidney disease.
5) Blood urea nitrogen: It is also called BUN which is also increased in kidney disease.
6) Serum electrolyte – If any symptoms suggestive of electrolyte imbalance then serum electrolyte can be measured too.
7) Serum calcium level – If the calcium level is low then it is important to do further investigation to find the cause for low calcium level which can include parathyroid hormone investigation too.
URINE TEST TO DETERMINE RENAL FUNCTION TEST :
1) COLOR: Urine color can be changed in some diseases such as if haematuria is present it can be red or cola color. The color change can also be due to medicine like rifampicin or also can be due to some food items like beetroot, or food coloring. Alkaptonuria can result in black or brown urine and myoglobin can result in black urine on standing.
2) SMELL: Foul smell in urine can be present in urinary tract infections.
3) VOLUME: Urine volume varies from the individual person as it depends on various factors like the amount of water consumption, and weather conditions. Normally a person’s urine output in 24 hours can be in between 800-2500 ml. If the urine output is less then it points towards kidney disease. High and frequent urine output can be due to infections or diabetes.
4) URINE PH – Normal urine pH ranges between 4.5 to 6.5 and if urine is acidic then the patient can be suffering renal tubular acidosis. Alkaline urine is found in some bacterial infections and cystinuria.
5) GLYCOSURIA – In cases of high and uncontrolled diabetes, urine examination can show glucose which is known as Glycosuria.
6) PROTEINURIA- Excretion of protein in urine can be seen in nephrotic syndrome, urinary tract infections, uncontrolled diabetes, and other diseases.
7) MICROALBUMINURIA – Albumin excretion through urine should also be evaluated further to find the cause.
8) URINARY CRYSTALS – It can be seen in patients suffering from uric acid, calcium oxalate, and calcium phosphate crystal in urine which can point towards nephrolithiasis too.
9) URINARY SPECIFIC GRAVITY- If the person is having Glycosuria or proteinuria then it is most likely that the specific gravity will be higher.
10) URINARY CAST – It can be present in some normal people, athletic people, and also in the patient suffering from fever, cardiac failure, and also in parenchymal renal disease.
11) URINARY KETONE BODIES: It is found in the patient suffering from uncontrolled diabetes which is progressing towards diabetic ketoacidosis.
RENAL STUDIES –
Renal Imaging Studies for renal function test –
various renal imaging techniques are available to assess renal function test.
1) X-RAY KUB – KUB ( kidney ureter bladder) x-ray is beneficial for finding renal stones, especially radio-opaque stones.
2) ULTRASOUND – Abdominal ultrasound is helpful to find kidney size, renal stones, hydronephrosis, any renal mass, or any stricture in the ureter.
3) ULTRASOUND DOPPLER – It can be done to check the renal blood flow, urinary flow, any thrombus in the renal artery or vein, renal atherosclerosis, and renal artery stenosis. Color Doppler is available too for further investigation.
4) CT SCAN- It is an important tool for kidney imaging that helps in the detection of various kidney diseases such as kidney stones, renal masses, renal structure studies, or any renal carcinoma. GFR (GLOMERULAR FILTRATION RATE) can be estimated too.
5) MRI – In some cases, MRI cases can beneficial but still CT scan is considered a better option as MRI is expensive too comparing to CT SCAN.
6) PET SCAN – It is mostly helpful in the detection of any renal carcinoma.
RENAL BIOPSY FOR RENAL FUNCTION TEST –
It is also a mode of investigation for renal function tests.
It is a process of taking a tissue sample from the kidney and doing further studies to find the causes of symptoms and make a diagnosis. This method is mostly used when the doctor is not able to make a confirmatory diagnosis from the above mentioned investigation process.
SUMMARY
Various types of blood tests, urine tests, and imaging techniques are available along with history taking which can help the doctor to make a confirmatory diagnosis of the disease and develop an effective treatment plan that can be given to the patient to save the kidney from any further damage.